Source(google.com.pk)
Cancer Of The Throat Biography
Throat cancer is a general term that applies to cancer that develops in the throat (pharyngeal cancer) or in the voice box (laryngeal cancer). The two cancers are often linked together due to fact that the voice box is located directly below the throat. Within the voice box and throat there are more specific types of cancer. Nasopharyngeal cancer is cancer that begins in the nasopharynx or the part of the throat located just behind the nose. Oropharyngeal cancer begins in a part of the throat right behind your mouth, that includes the tonils. Hypopharyngeal cancer begins in the lower part of your throat just above your esophagus and windpipe. Glottic cancer is cancer of the vocal chords. Lastly supraglottic cancer and subgottic cancer begin in the upper (spraglottic) and lower portion (subglottic) of your voice box. Each of the separate types has a link to its own symptoms, some of which include a cough, change in voice, difficulty swallowing, ear pain, sore throat, unintentional weightless, or a lump or sore that doesn’t heal.
Throat cancer occurs when cells in your throat develop genetic mutations, causing cells to grown uncontrollably and continue living after healthier cells would normally die. What causes the mutations is generally unknown but risk factors show a link to carcinogens like alcohol and tobacco.
Carcinogenesis is literally the creation of cancer. Proto-oncongenes are genes that promote cell growth and mitosis. Tumor suppressor genes discourage cell growth or temporarily halt cell decision to carry out DNA repair. What a mutation is to occur in a proto-oncogene (becomes oncogene) damage would be suppressed by normal mitosis control and tumor suppressor genes. One mutation tumor suppresses would not cause caner either because of many backup genes that duplicate it’s functions. Only when enough proto-oncogenes have been mutated into oncogenese and enough tumor suppressor genes are deactivated or damaged signals for cell growth overwhelm the signals to regulate it and cell growth quickly spirals out of control.
One’s risk of throat cancer increases if they smoke or drink alcohol. People who use tobacco and alcohol together are at more of risk then those who use them separately. Some research also suggests that leukoplakia (white patches in mouth) or erythorkplakia (red raised patches in the mouth) may also be throat cancer risk factors. Most throat cancers develop in adults older then 50 and men are ten times more likely the women. Ethnicity may also be a factor with African American men in the U.S. being found to be at a 50% higher risk of throat cancer than Caucasian men.
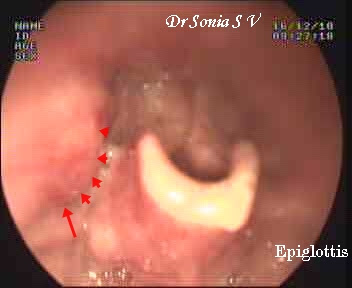
When it comes to diagnosing throat cancer doctors have several different options. Doctors may use a special lighted scope (endoscope) to get a closer look at throat during a procedure called an endoscopy. And Laryngoscope is another type of scope that can be inserted in your voice box. If abnormalities are found you can pass a surgical instrument through the scope to collect a tissue sample (biopsy). Imaging tests, including X-ray, computerized tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography may help doctors determine the extent of your cancer beyond the surface of your throat or voice box. Once diagnosed, the next step is to determine the extent or stage of the cancer. Stages help to determine treatment options per patient. Stages are characterized by roman numerals I- IV and each subtype ahs its own criteria for each stage.
Treatment options are then based on many factors: location and stage of throat cancer, type of cells involved, overall heath, and personal preference. Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles like X-rays to deliver radiation to the cancer cells causing them to die. Another option is surgery. Depending on the stage or type of cancer the procedures vary. For cancer that is confined to the surface of the throat or the vocal chords may be treated surgically using endoscopes. For serious cases of throat cancer there are procedure to remove all or part of ones throat or voice box. Other options include: chemotherapy, uses chemicals to kill cancer cells, and targeted drug therapy, which treats throat cancer by altering specific aspects of cancer cells that fuel their growth.
Rehabilitation after treatment for throat cancer is tough. Treatment often causes compilations that may require working with specialists to regain the ability swallow, eat solid foods, and talk. This terrible disease is one that I would wish on nobody, and hopefully one day we will find the cure.














Cancer Of The Throat Biography
Throat cancer is a general term that applies to cancer that develops in the throat (pharyngeal cancer) or in the voice box (laryngeal cancer). The two cancers are often linked together due to fact that the voice box is located directly below the throat. Within the voice box and throat there are more specific types of cancer. Nasopharyngeal cancer is cancer that begins in the nasopharynx or the part of the throat located just behind the nose. Oropharyngeal cancer begins in a part of the throat right behind your mouth, that includes the tonils. Hypopharyngeal cancer begins in the lower part of your throat just above your esophagus and windpipe. Glottic cancer is cancer of the vocal chords. Lastly supraglottic cancer and subgottic cancer begin in the upper (spraglottic) and lower portion (subglottic) of your voice box. Each of the separate types has a link to its own symptoms, some of which include a cough, change in voice, difficulty swallowing, ear pain, sore throat, unintentional weightless, or a lump or sore that doesn’t heal.
Throat cancer occurs when cells in your throat develop genetic mutations, causing cells to grown uncontrollably and continue living after healthier cells would normally die. What causes the mutations is generally unknown but risk factors show a link to carcinogens like alcohol and tobacco.
Carcinogenesis is literally the creation of cancer. Proto-oncongenes are genes that promote cell growth and mitosis. Tumor suppressor genes discourage cell growth or temporarily halt cell decision to carry out DNA repair. What a mutation is to occur in a proto-oncogene (becomes oncogene) damage would be suppressed by normal mitosis control and tumor suppressor genes. One mutation tumor suppresses would not cause caner either because of many backup genes that duplicate it’s functions. Only when enough proto-oncogenes have been mutated into oncogenese and enough tumor suppressor genes are deactivated or damaged signals for cell growth overwhelm the signals to regulate it and cell growth quickly spirals out of control.
One’s risk of throat cancer increases if they smoke or drink alcohol. People who use tobacco and alcohol together are at more of risk then those who use them separately. Some research also suggests that leukoplakia (white patches in mouth) or erythorkplakia (red raised patches in the mouth) may also be throat cancer risk factors. Most throat cancers develop in adults older then 50 and men are ten times more likely the women. Ethnicity may also be a factor with African American men in the U.S. being found to be at a 50% higher risk of throat cancer than Caucasian men.
When it comes to diagnosing throat cancer doctors have several different options. Doctors may use a special lighted scope (endoscope) to get a closer look at throat during a procedure called an endoscopy. And Laryngoscope is another type of scope that can be inserted in your voice box. If abnormalities are found you can pass a surgical instrument through the scope to collect a tissue sample (biopsy). Imaging tests, including X-ray, computerized tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography may help doctors determine the extent of your cancer beyond the surface of your throat or voice box. Once diagnosed, the next step is to determine the extent or stage of the cancer. Stages help to determine treatment options per patient. Stages are characterized by roman numerals I- IV and each subtype ahs its own criteria for each stage.
Treatment options are then based on many factors: location and stage of throat cancer, type of cells involved, overall heath, and personal preference. Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles like X-rays to deliver radiation to the cancer cells causing them to die. Another option is surgery. Depending on the stage or type of cancer the procedures vary. For cancer that is confined to the surface of the throat or the vocal chords may be treated surgically using endoscopes. For serious cases of throat cancer there are procedure to remove all or part of ones throat or voice box. Other options include: chemotherapy, uses chemicals to kill cancer cells, and targeted drug therapy, which treats throat cancer by altering specific aspects of cancer cells that fuel their growth.
Rehabilitation after treatment for throat cancer is tough. Treatment often causes compilations that may require working with specialists to regain the ability swallow, eat solid foods, and talk. This terrible disease is one that I would wish on nobody, and hopefully one day we will find the cure.
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat

Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
Cancer Of The Throat
No comments:
Post a Comment